题目描述 链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/3da4aeb1c76042f2bc70dbcb94513338来源:牛客网
设计一个数据结构,实现LRU Cache的功能(Least Recently Used – 最近最少使用缓存)。它支持如下2个操作: get 和 put。
int get(int key) – 如果key已存在,则返回key对应的值value(始终大于0);如果key不存在,则返回-1。
请特别注意“使用”的定义:新插入或获取key视为被使用一次;而将已经存在的值替换更新,不算被使用。
限制:请在O(1)的时间复杂度内完成上述2个操作。
题解和思路 维护一个双向链表,链表的元素即是键值对,使用一个元素就把他放到头部,这样当容量不够时,链表结尾的元素即是最近最久没使用过的元素,将其删除即可
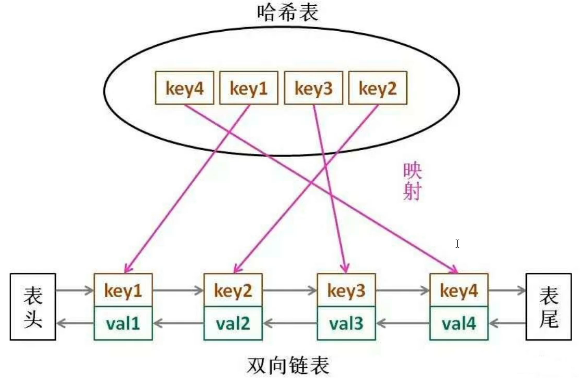
链表的删除和添加是非常方便的,可以达到O(1)的复杂度,但是查询就比较慢了,为了弥补这个不足,我们再额外维护一个散列表,便于查询,双向链表和散列表一定要对照,如图
关键点
一个最大的容量、get()和put()两个API
必须保证都是O(1)的时间复杂度
上一次访问的元素在第一个
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Scanner;class Node {public int key;public int val;public Node pre,next;int key,int val){this .key = key;this .val = val;class DoubleList {private Node head;private Node tail;private int size;this .head = new Node (0 ,0 ); this .tail = this .head;this .size = 0 ;public void addFirst (Node node) {Node temp = head.next;if (temp!=null ){this .size ++;if (size == 1 ){this .tail = node;public Node removeLast () {if (this .size==0 ){return null ;else {Node temp = this .tail;this .tail = tail.pre;null ;this .size --;return temp;public void remove (Node node) {if (node==this .tail){else {this .size --;public int size () {return this .size;class LRUCache {private DoubleList doubleList = new DoubleList ();private Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap <>();private int capacity;int capacity){this .capacity = capacity;public void put (int key,int val) {if (this .capacity <= 0 ){return ;Node node = new Node (key,val);Node origin = map.get(key);if (origin != null ){else if (doubleList.size() == capacity){Node last = doubleList.removeLast();else {public int get (int key) {Node result = map.get(key);if (result==null ) {return -1 ;else {return result.val;public class Main {public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);int ca = sc.nextInt();LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache (ca);while (sc.hasNext()){String order = sc.next();if ("p" .equals(order)){int key = sc.nextInt();int value = sc.nextInt();else if ("g" .equals(order)){int key = sc.nextInt();int res = lruCache.get(key);
测试数据 输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2
输出 说明 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 //Cache容量为2